Sweating is a natural and essential process that helps regulate body temperature. But if you find yourself sweating far more than usual, even without heat, exercise, or stress, you may be dealing with excessive sweating, medically known as hyperhidrosis. This condition goes beyond normal perspiration and can significantly affect daily comfort, confidence, and quality of life.
Understanding why it happens is the first step toward managing it effectively.
What Is Hyperhidrosis?
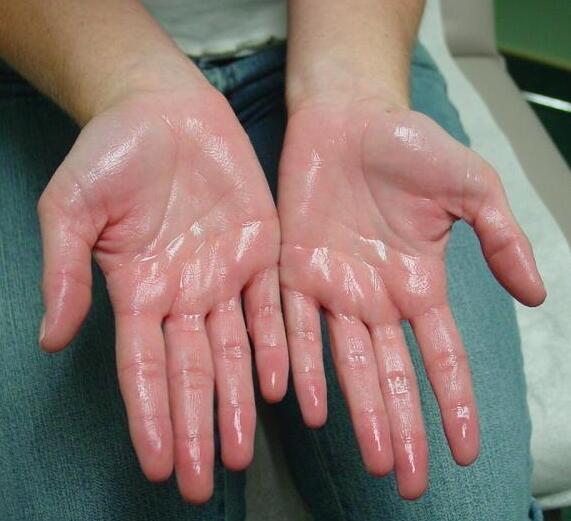
Hyperhidrosis is a medical condition in which the body produces excessive sweat beyond what is required for temperature regulation. It may affect one or multiple areas of the body and often occurs without obvious triggers.
Medical Reasons Behind Excessive Sweating
1. Overactive Sweat Glands
In many people with hyperhidrosis, sweat glands are overstimulated by the nervous system. Even minor signals can trigger intense sweating, especially in areas like the palms, soles, underarms, and face.
2. Primary Hyperhidrosis (No Underlying Disease)
This is the most common form and usually:
- Starts in childhood or adolescence
- Affects specific areas (hands, feet, underarms, face)
- Occurs symmetrically (both hands or both feet)
- Is not related to another medical condition
Genetics often play a role, meaning it can run in families.
3. Secondary Hyperhidrosis (Linked to Medical Conditions)
In some cases, excessive sweating is a symptom of an underlying health issue, such as:
- Thyroid disorders
- Diabetes
- Hormonal imbalances
- Menopause
- Infections
- Certain neurological conditions
This type often causes generalized sweating, including during sleep.
4. Hormonal Changes
Fluctuations in hormones can overstimulate sweat glands. This is commonly seen during:
- Pregnancy
- Menopause
- Puberty
- Thyroid dysfunction
5. Anxiety and Stress Response
While anxiety doesn’t cause hyperhidrosis, it can intensify sweating. The body’s “fight-or-flight” response activates sweat glands, especially on the palms, soles, and face.
6. Certain Medications
Some medications can trigger excessive sweating as a side effect, including:
- Antidepressants
- Pain medications
- Hormonal therapies
- Fever-reducing drugs
If sweating begins after starting a new medicine, medical evaluation is advised.
7. Obesity and Metabolic Factors
Excess body weight can increase sweating due to:
- Increased heat production
- Reduced heat dissipation
- Greater strain on temperature regulation
However, hyperhidrosis can occur even in individuals with a normal body weight.
Areas Commonly Affected by Hyperhidrosis
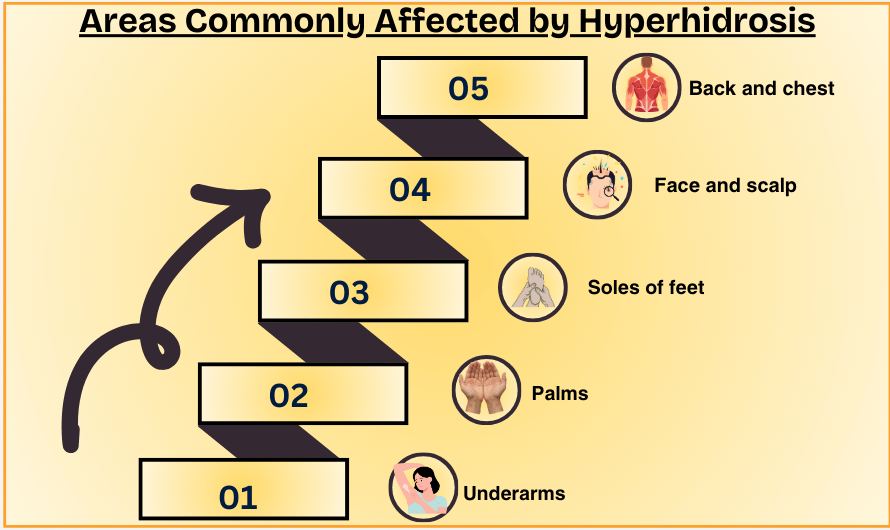
- Underarms (axillary hyperhidrosis)
- Palms of hands (palmar hyperhidrosis)
- Soles of feet (plantar hyperhidrosis)
- Face and scalp
- Back and chest
When Is Excessive Sweating a Medical Concern?
You should consider consulting a doctor if:
- Sweating occurs without heat or activity
- It interferes with work or social life
- You experience night sweats
- Home remedies and antiperspirants don’t help
- Sweating causes skin infections or irritation
Can Excessive Sweating Be Treated?
Yes. Hyperhidrosis is highly manageable. Depending on severity and cause, treatment options may include:

- Medical-grade antiperspirants
- Prescription topical treatments
- Oral medications (in selected cases)
- Botox injections for excessive sweating
- Advanced non-surgical procedures
A Cosmetologist can create a personalized treatment plan after proper evaluation.
Final Thoughts
If you’ve ever wondered, “Why do I sweat so much?”—you’re not alone. Excessive sweating is not a hygiene issue or something you have to live with. It is a real medical condition with effective solutions available today. Early diagnosis and the right treatment can greatly improve comfort, confidence, and overall well-being.


